
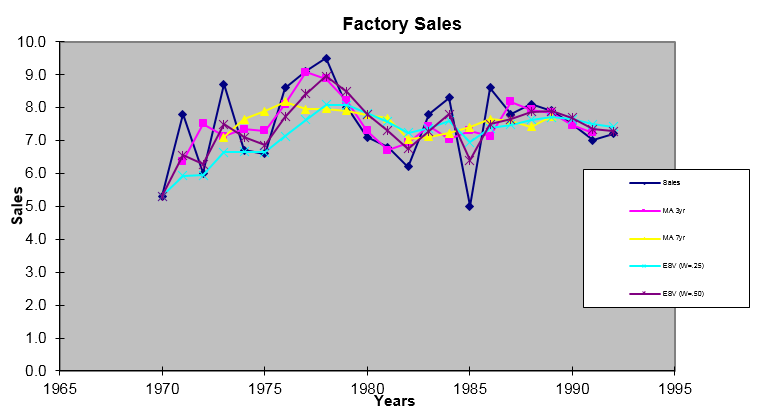
The lack of price data from previous days makes it impossible to calculate the EMA. It usually happens when we need the price chart for a newly listed company. But what if there is no data on the previous EMA. In EMA calculations we use K* (current price – Previous EMA) + Previous EMA when we need the previous period’s EMA. Why do we need the weighting factor? By definition, EMA gives more weight to recent prices. K is equal to 2/(n+1), where n is the selected time period.
Here, the formula has used the weighting factor denoted by K. The above calculation is done for the calculation of EMA for the first time when no earlier EMA data is available. Using this formula, it can be easily determined that the 21-day EMA is actually a 9% EMA. The formula for converting time periods to exponential moving average is Exponential percentage = 2/ + 1 With this formula, it can be proven that the 9 percent moving average is equivalent to 21-day EMA. The formula for converting exponential percentage to time period is Time periods = -1 The percentage can be converted to time periods EMA, and a 9% EMA can be converted to 21.2-day EMA or 21-day EMA. Today’s closing price*9/100 + Yesterday’s moving average*91/100 = Today’s price*o.09 + Yesterday’s moving average*0.91īut traders always prefer working with time periods instead of percentages. Then, add this to the moving average of yesterday by 91% (100-9). It was done because EMA gives more weight to current market prices.įor example, to calculate a 9% exponential moving average of stock, we should multiply today’s closing price by 9%. Primarily, the exponential moving average was calculated by applying a percentage of the current day’s closing price to the moving average of the previous day. How is Exponential Moving Average Calculated? The longer EMA is affected by large price changes. We can conclude that the response is faster for EMA with shorter time periods.
The 100-period EMA line is so slow to react that all the price changes shown above affected the 100-period EMA line very little and the price changes are only reflected on the line by changing the slope. The chart shows the 10-period EMA line in red and the 100-period EMA line in black. We can see the 10-period EMA is clinging close to the price candles and responding faster to price changes.īut the 100-period EMA line is sluggish, moving very little with all the price changes shown above. Shown above is the chart of Nifty 50 with an overlay of 1an 0-day EMA and 100-day EMA lines. For example, a 10-day EMA line moves almost along with the price action and reacts faster than a 100-day EMA. But the lag is still there.ĭue to the lag, the shorter period EMA line responds faster than that with a longer period. By giving more weight to recent data points, the amount of lagging is found to be less in the case of EMA. The introduction of EMA solved this problem a little. Therefore, there is a tendency of lagging found with the moving average lines. Lag Factor in EMAĪll kinds of moving averages are calculated using the historical price data points. There’s a minimum lag factor involved in it due to the application of more weight on a most recent price data point. The result of this calculation is represented by a curved line known as the exponential moving average (EMA) line. Usually, the exponential moving average (EMA) is calculated by taking in the closing prices as with most other types of moving averages. The exponential moving average or EMA is the moving average of over a specific time period which is calculated by giving more weight to the most recent price data, making the price average react faster to price changes. What is the Exponential Moving Average (EMA)? When the EMA is used with other indicators, the signals become more accurate and powerful. The exponential moving average gives us an idea of support and resistance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
